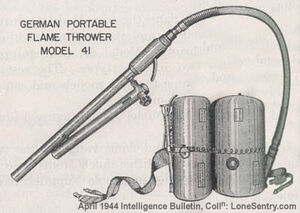
The German Flammenwerfer 41
The Flammenwerfer 41 was a German-made flamethrower used during World War II, firing a searing stream of liquid hell. It was the Special Weapon of the Nazi SS.
Description
The Flammenwerfer 41, or FmW 41, was modified from the older Flammerwerfer 35, making it lighter (as the FmW 35 weighed about 79 lbs). It had two horizontal tanks that strapped onto the user's back, one of them holding 3 gallons of fuel, the other being a Nitrogen tank used as a propellant. The fuel used was flaming oil (Flammöl 19), a mixture of gasoline and tar, which made it heavier and increased the firing range, as well as making the flaming mixture stick to anything it touched. It was ignited by a hydrogen torch located within the muzzle.
During the later stages of its service life, the trigger and muzzle sections were modified so as to resemble a standard infantry rifle in an attempt to disguise users and prevent them from being singled out by enemy snipers.
Stats
- Range: 80 feet
- Maximum Range: 105 to 130 feet
- Weight: 48 lbs
- Ammo: Gasoline and tar
- 10-second bursts
Use
Flamethrowers were introduced by the German Empire in WWI in order to clear trenches and buildings. [1]
The Flammenwerfer earned the nickname "skinsteal" because use of this weapon at close range often resulted in severe skin loss. The weapon had an effective range of 25 meters (83 feet) and a maximum range of 30 m (100 ft).
Trivia
- N-Stoff (Substance N), officially known as Chlorine Trifluoride, was a flammable chemical that the Nazis attempted to use for napalm and flamethrowers. The Nazis discarded the chemical weapon; as even they thought it was too dangerous.
- This was the third weapon noted to be illegal in the United States, after the Ballistic Knife and the LPO-50 Flamethrower
